
Dracaena trifasciata (left) & its 'Laurentii' cultivar on the right.
Contents
- Top Tips
- Location, Water, Humidity & Fertilisation
- Common Issues
- Origins, Temperature, Propagation, Repotting & Toxicity.
Are you struggling to find the answer to your specific plant issue? Book a 1-to-1 video call with THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™, the website's friendly author, to overcome and address your niggling problem! Available on iMessage, WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger & more.
Top Tips & Info
- Care Difficulty - Easy
- Provide a bright, indirect location away from more than two hours of sunlight per day. Sansevieria are a great choice for a shady statement plant, as long as you remember to keep them under-watered. Those seeking Sansevieria to grow in a sun-filled location must build up their plant's tolerance to the sun over the course of the next eight weeks to avoid sun-scorch.
- Sansevieria must endure periods of droughts between waters - if you're stuck with when to water it, think of the ukhouseplants' phrase of 'Drenches Between Droughts'.
- Be careful when watering - allowing excess moisture to sit in the cubbyholes of the lower stem will result in diseases such as southern blight or basal rot.
- Feed every two months using either a 'Cactus & Succulent' or 'Houseplant' labelled concentrate fertiliser that's diluted down.
- Repot every three years during the spring, using a 'Cactus & Succulent' labelled potting mix - this is the perfect time to perform rhizomatous propagation. (Scroll down to 'Propagation' for more.
Location & Light - 🔸🔸🔸
In terms of light requirements, Sansevieria are versatile and therefore can be grown in both dark rooms & sunny windowsills. As their leaves point vertically and face laterally across the room, they can perform photosynthesis even in the darkest of rooms. If you're someone who's interested in keeping their Sansevieria in a sunnier location, make sure you build-up their tolerance to the heightened exposure by increasing the hours spent in the direct sun by an hour each week. (Example: 1st week it can spend one hour in the sun and on the second week it can spend two hours, and so forth until it's comfortable with your chosen location).
Remember: The darker the location, the less frequently you want to water the plant. Root Rot is a common problem with dark-grown plants, so ensure your soil becomes fully dry before dehydration!
Water - 🔸
The ukhouseplants saying, 'drenches between droughts', strongly applies to your Sansevieria. Not only will continuous soil moisture destroy their root systems, it'll also breakdown the new leaves from emerging from under the soil via their rhizomes (root-stems). Allow all of the soil to thoroughly dry out in between waters in the growing period, reducing this further in the autumn and winter. Under-watering symptoms include a weakened grey stem, yellowing leaves, little to no growth and dry, crispy patches forming on the leaf edges; these issues are usually caused by too much light/heat or forgetfulness. Remember, the brighter the location, the more watering you'll need to do. Over-watering symptoms include a weakened grey stem, leaves that have a rotten base, no new growth, yellowing leaves and plant death. The differences between under and over-watering are very similar, with a rotten root ball stopping the plant soak up vital moisture and nutrients, leaving you with wilted grey leaves.
Humidity -
This is not a necessity; however, a quick hose down from time to time will hydrate the leaves and wash away dust or potential pests.
Fertilisation - 🔸
While using a diluted concentrate fertiliser, feed every two months using either a 'Cactus & Succulent' or a 'Houseplant' labelled fertiliser. As Sansevieria naturally grow in nutrient-leached soils, irregular feeding won't be a serious problem to their health. Never directly apply a 'Ready-to-Use' (RTU) without a pre-water first as this may lead to the burning or roots though!
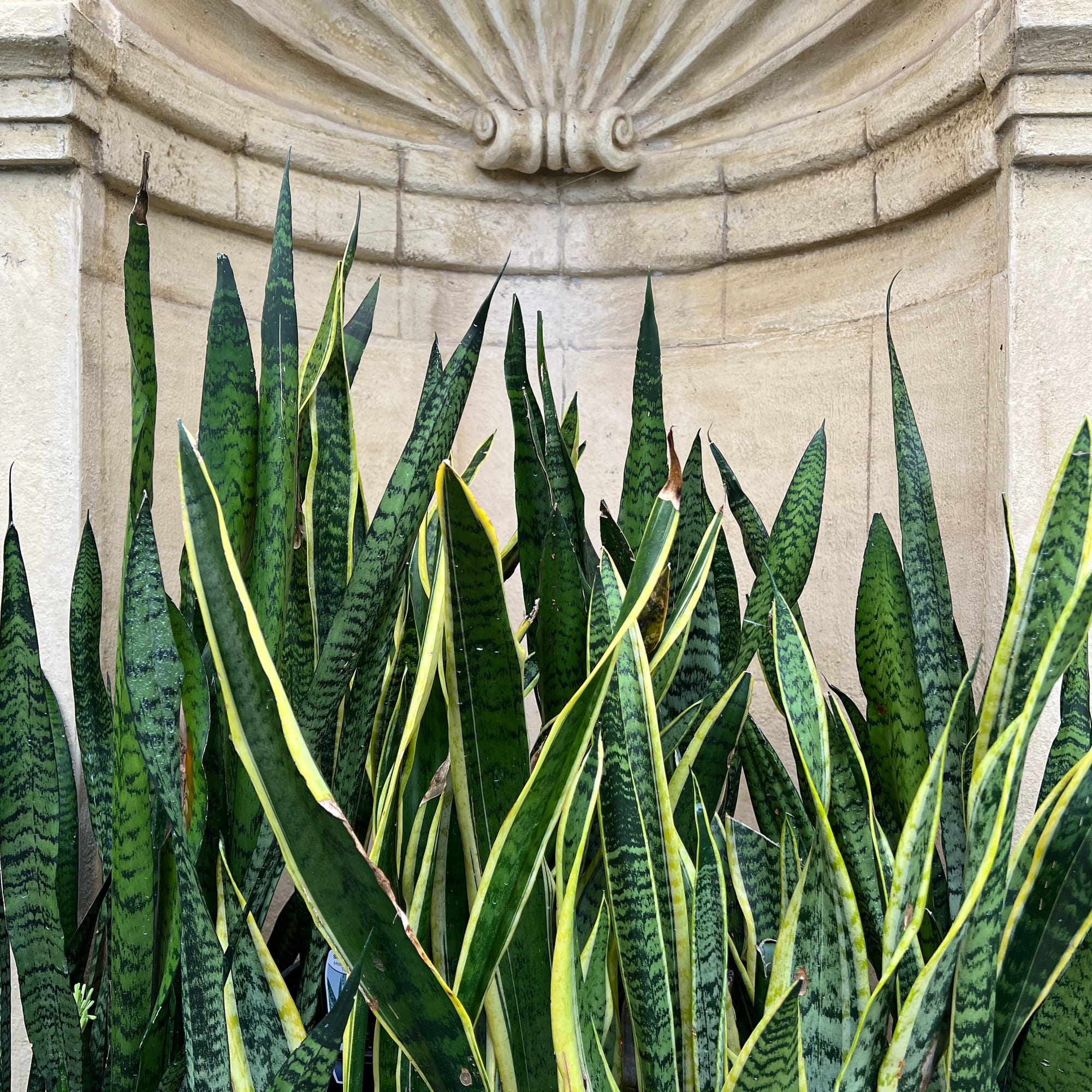
 Sansevieria zeylanica
Sansevieria zeylanica
Common Issues with Sansevieria
Orange or yellow root systems are signs of a healthy root system and therefore shouldn't concern the grower. See Image 6 for an example of a healthy root system. (Via the 'Propagation' section below).
Root rot is a common issue with specimens sat in too moist or waterlogged soil for long periods. Symptoms include rapidly yellowing leaves, stunted growth and a rotten brown base. Take the plant out of the pot and inspect health below the soil line. If the roots sport a yellow/orange tinge, you're good to go, but if they're brown and mushy, action must be taken immediately. More information about addressing root rot can be found on this link.
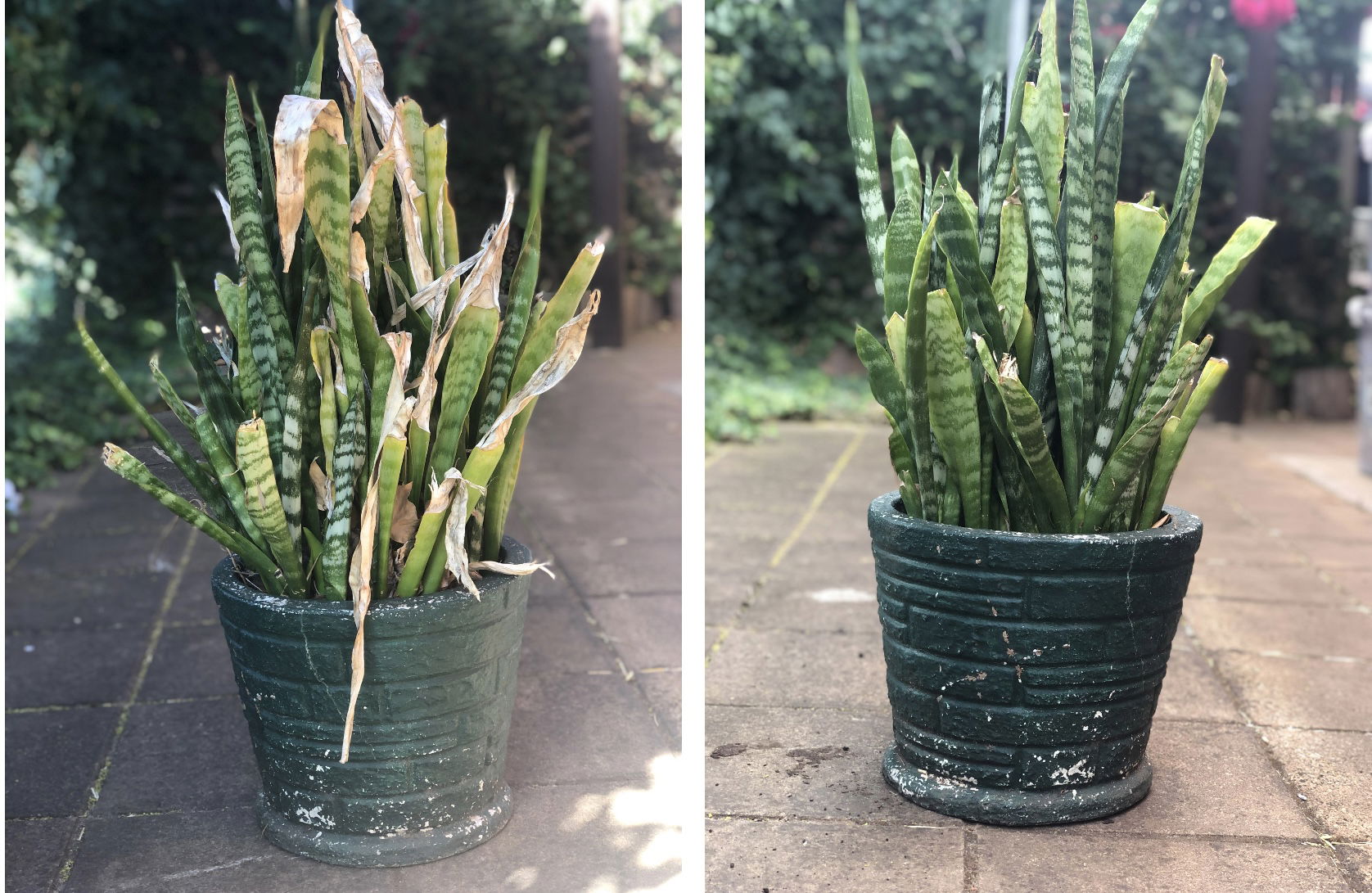 Curled leaves and dried brown edges are the result of too little water and over-exposure to the sun. Although Sansevieria can naturally do well in sun-filled locations, those that haven't acclimatised to the harsh rays will show signs of sun-scorch and environmental shock. Prolonged exposure will significantly speed the process of dehydration, so consider transplantation into a bigger pot in the spring to wrap the roots around moister soil. The image above shows before & after being treated for sun scorch.
Curled leaves and dried brown edges are the result of too little water and over-exposure to the sun. Although Sansevieria can naturally do well in sun-filled locations, those that haven't acclimatised to the harsh rays will show signs of sun-scorch and environmental shock. Prolonged exposure will significantly speed the process of dehydration, so consider transplantation into a bigger pot in the spring to wrap the roots around moister soil. The image above shows before & after being treated for sun scorch.
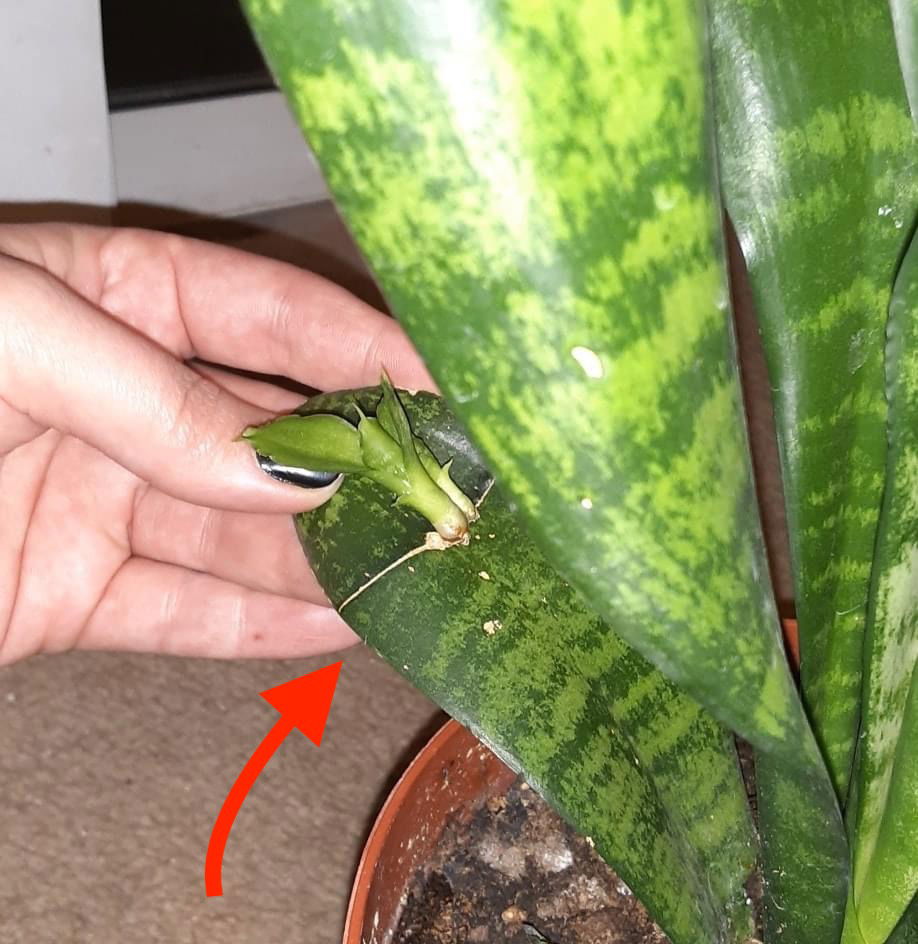 In some cases, small cracks in a Sansevieria's leaf may result in a small offset developing that can be propagated into its own 5cm pot when 7m (3 inches) in length.
In some cases, small cracks in a Sansevieria's leaf may result in a small offset developing that can be propagated into its own 5cm pot when 7m (3 inches) in length.
Directly pinpointing yellow leaves is rather hard due to the many different issues that could be at fault. Problems include watering-related abuse, too much or too little light, and fertilisation issues. If you'd like to speak to ukhouseplants regarding this issue, don't be afraid to book a 1-to-1 call with Joe Bagley to help guide you the process!
Never allow temperatures to dip below 8ºC (46ºF) as irreversible damage may occur in the likes of yellowed foliage and weakened growth. If this happens, remove the severely affected areas and immediately improve growing conditions - never cut through softened yellow growth, and only around brown, crispy sections. As rehabilitation can take several months because of its slow-growing nature, be sure to provide a stable location with better growing conditions to speed this process.
 If a blade becomes yellow but is still hardened at the base, it may be a sign of nitrogen-deficiency.
If a blade becomes yellow but is still hardened at the base, it may be a sign of nitrogen-deficiency.
Failed propagated stem cuttings - There are several reasons why the cuttings haven't rooted well, including: the time of year (spring or summer is best), its size (CHANGE cuttings should have at least three leaves), poor growing conditions (replace water weekly for water-propagated cuttings, and avoid over-watering for soil-grown plants), and its growing environment (a bright sunless windowsill and warmth is important).
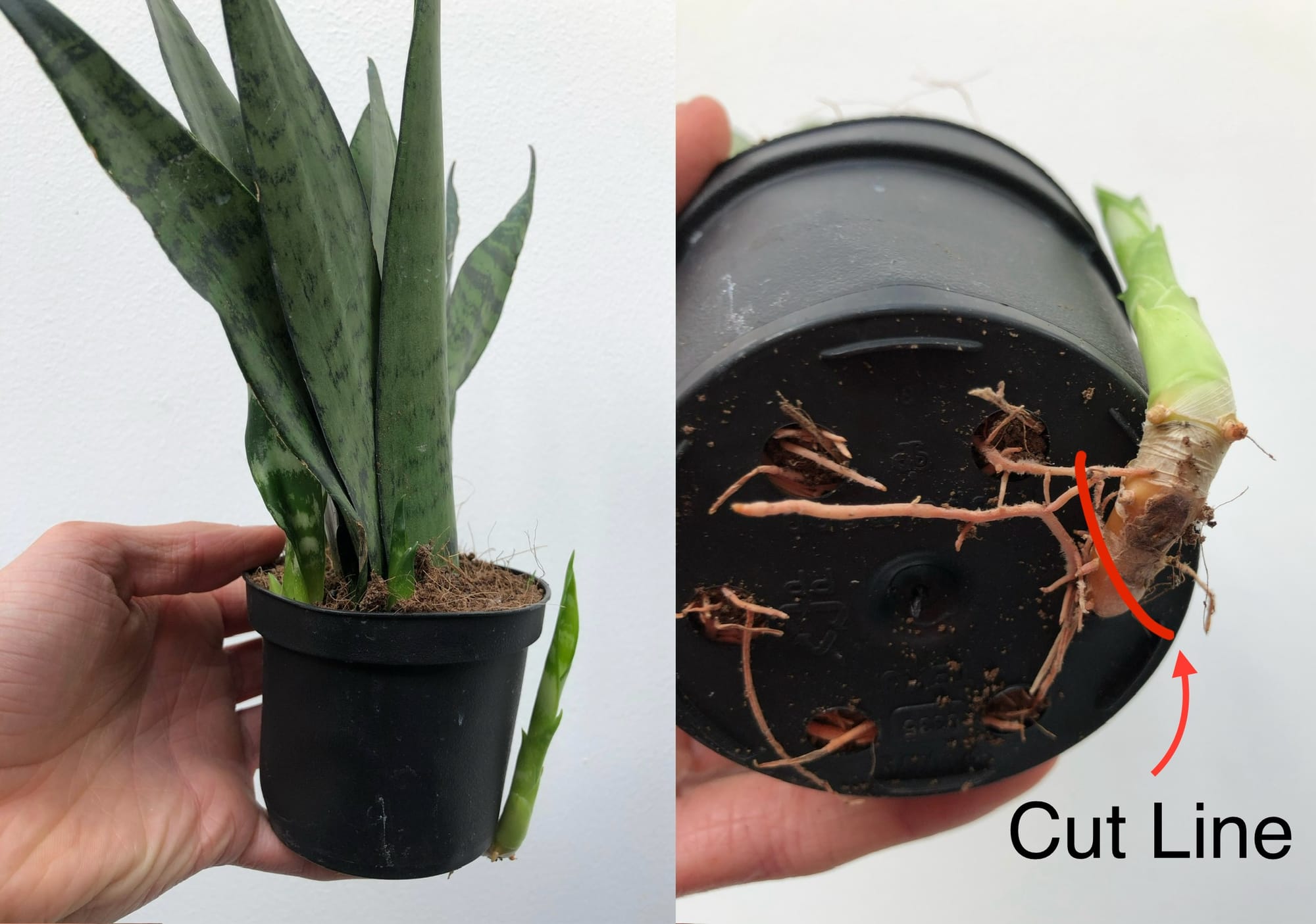

For sneaky offshoots like this, simply prune the cut it off via the red line and repot in a 10cm pot with 'Cactus' labelled soil. You could, however, repot the mother plant into a larger pot and place this loose cutting in with her to increase her overall size. It's your choice!
Origins
Sansevieria is a genus of around seventy species originating from the tropical regions of Africa, Madagascar and southern Asia. The most popular species, the Snake Plant (or Mother-In-Law's Tongue), mostly originates in areas surrounding Nigeria with its botanical name, S. trifasciata translating to 'three bundles' in Latin. The Sansevieria genus was discovered in the mid-1700s and is part of the Asparagaceae which holds members like Dracaena, Ponytail Palms and Aspidistra. There's considerable variation within Sansevieria, with some being arid-tolerate plants and others grown in tropical regions of South Asia. Although the genus is widely known to have been named after the Italian Prince of Sanseviero, it was initially penned in honour of Pietro Antonio Sanseverino, the Count of Chiaromonte in the 18th century. In 2017, a molecular study of the S. trifisciata conducted by David Mabberley found that the species, along with a few others, shared similar genetics to the genus, Dracaena. They were subsequently transferred into the latter genus in the same year so technically calling them Sansevieria is incorrect now!
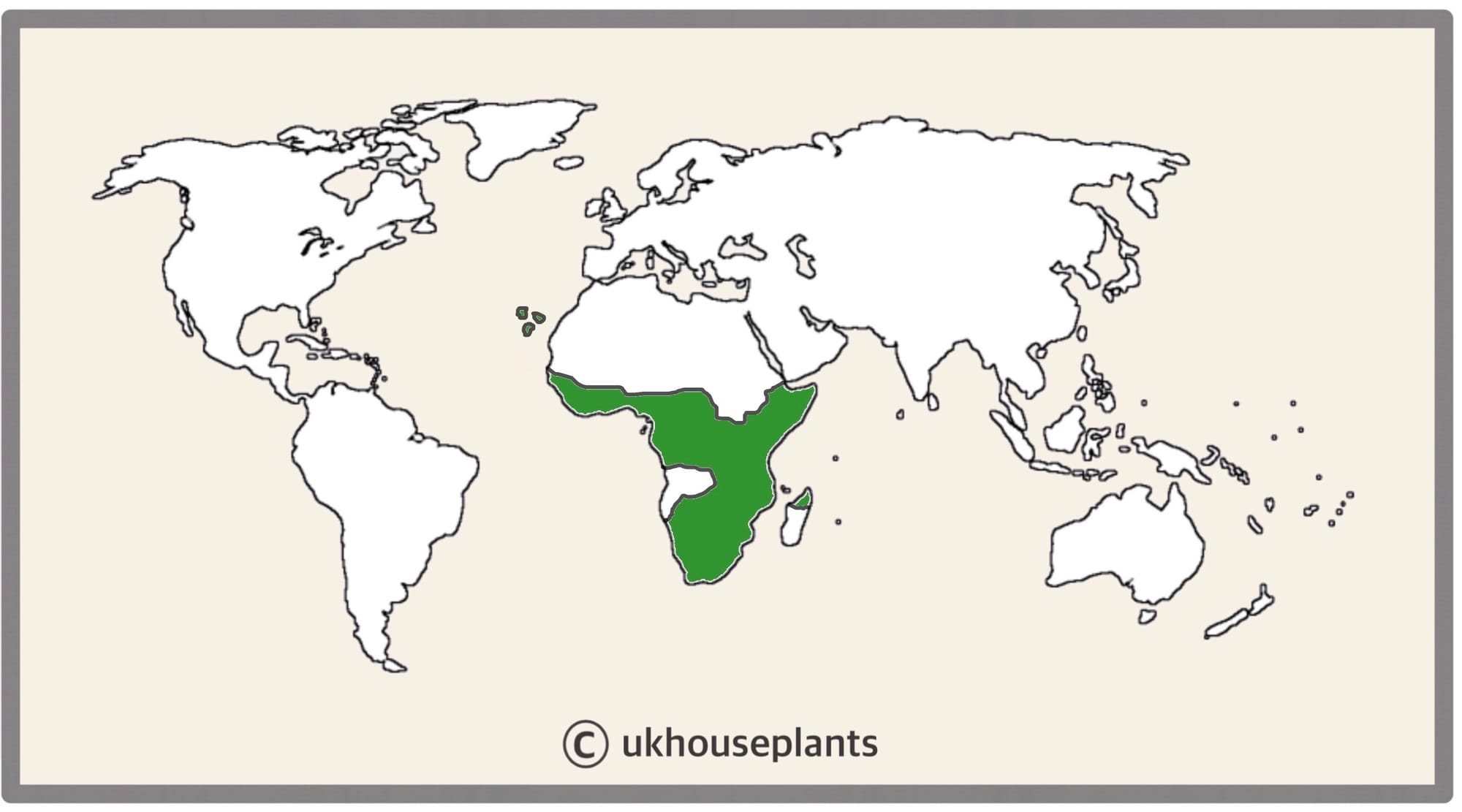 The Distribution of Sansevieria.
The Distribution of Sansevieria.
Temperature
10° - 32℃ (50° - 90℉)
H1b (Hardiness Zone 12) - Can be grown outdoors during the spring and summer in a sheltered location whilst nighttime temperatures are above 10℃ (50℉), but is fine to remain indoors, too. If you decide to bring this plant outdoors, don't allow it to endure more than an hour of direct sunlight a day as it may result in sun-scorch. Regularly keep an eye out for pests, especially when re-introducing it back indoors.
Spread
The overall size can be up to 1m in height and 0.5 m in width, with the blades' width reaching around 7cm. Ultimate height will take between 5 - 8 years to achieve when repotted biannually, with several new leaves unfurling per annum.
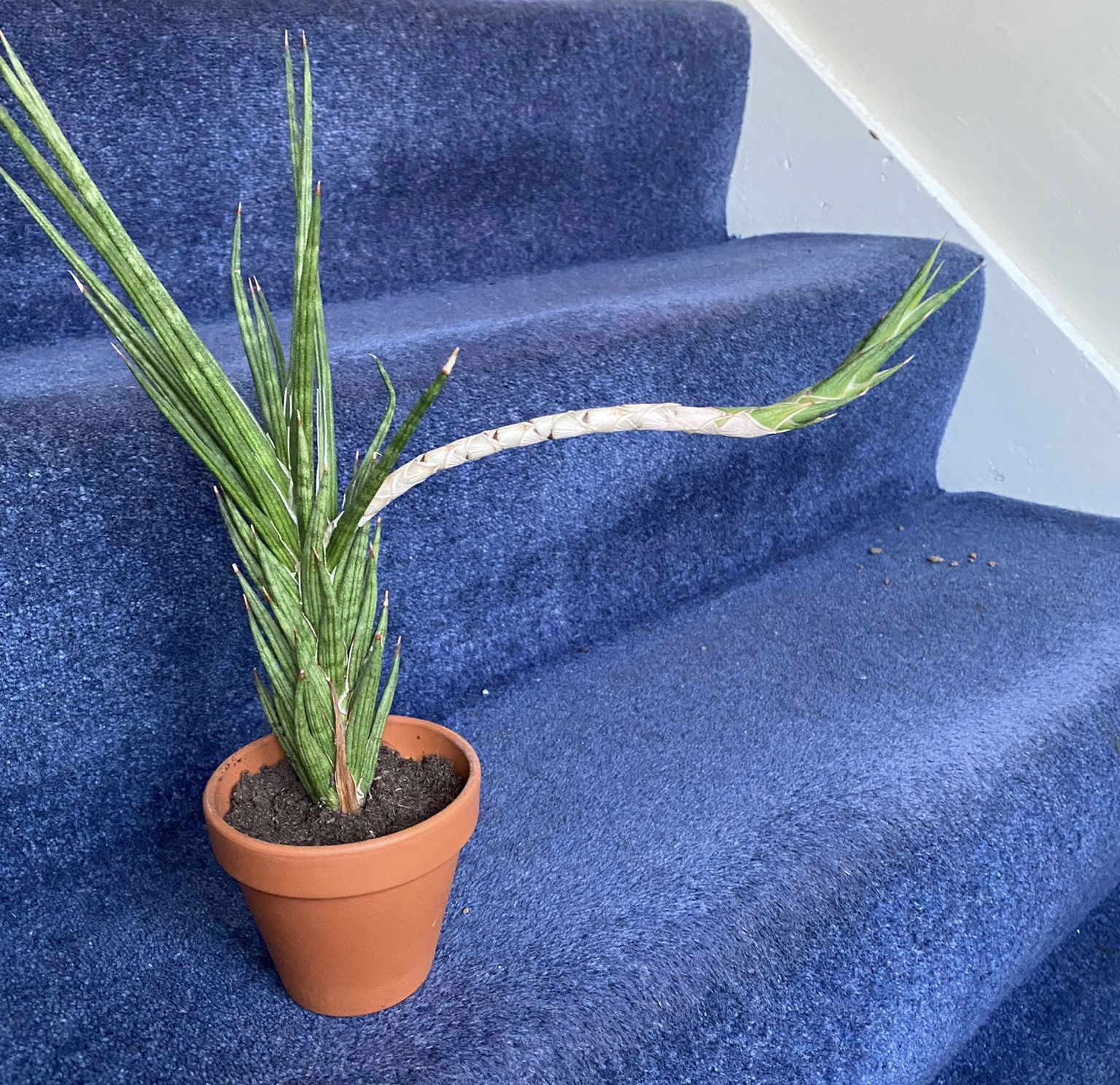 Feel free to propagate any 'runaway' growths by pruning 5cm (2 inches) below the pups' foliage and rooting in soil.
Feel free to propagate any 'runaway' growths by pruning 5cm (2 inches) below the pups' foliage and rooting in soil.
Pruning & Maintenance
Remove yellow or dying leaves, and plant debris to encourage better-growing conditions. While pruning, always use clean scissors or shears to reduce the chance of bacterial and fungal diseases. Never cut through yellowed tissue as this may cause further damage in the likes of diseases or bacterial infections. Remember to make clean incisions as too-damaged wounds may shock the plant, causing weakened growth and a decline in health.
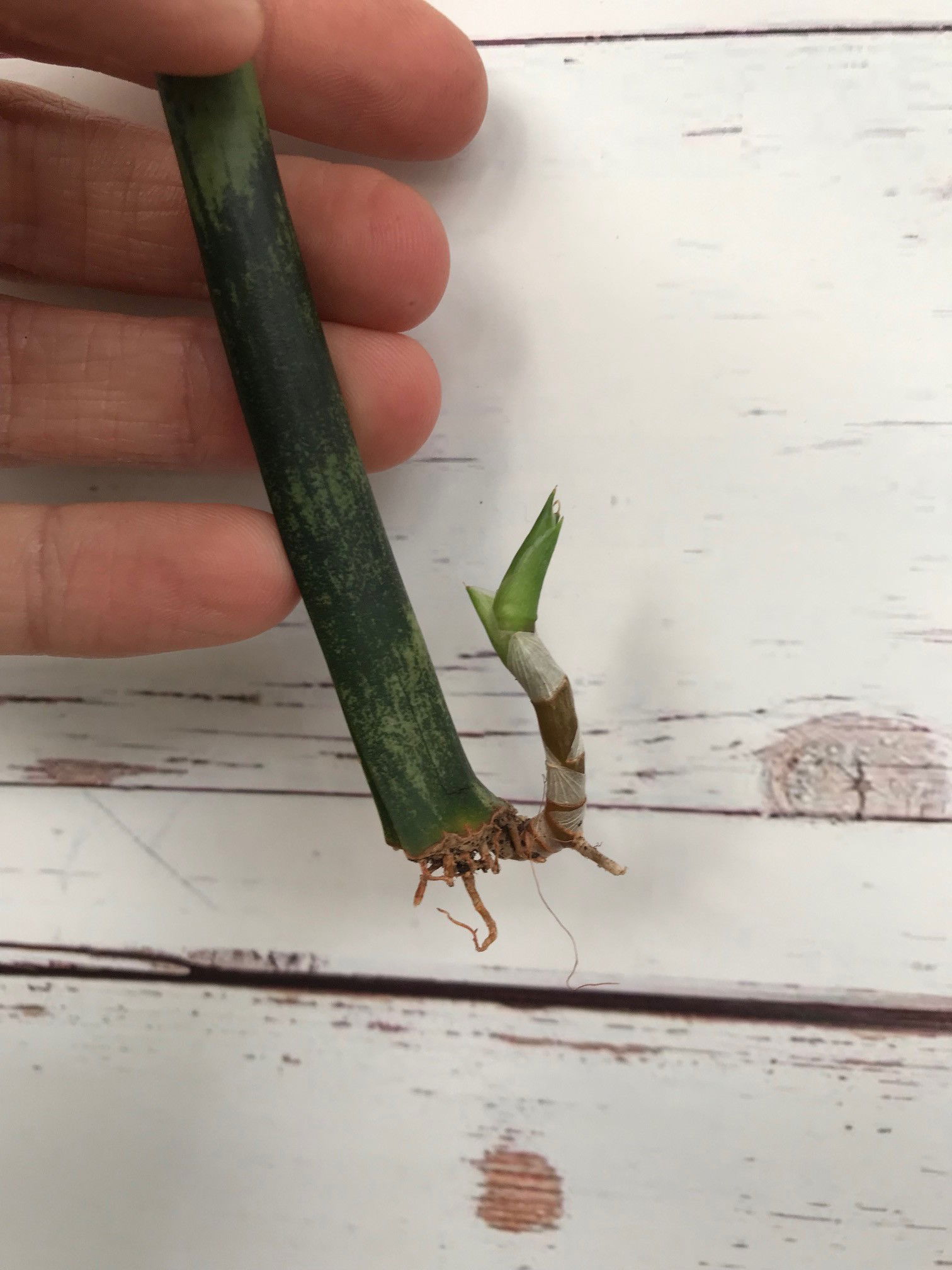 Here's a rhizomatous growth developing from the plant's base. The plant was originally propagated via a leaf cutting, which in turn is where the offsets will develop once calloused. Plant: Dracaena parva x D. suffruticosa 'Fernwood' (originally Sansevieria)
Here's a rhizomatous growth developing from the plant's base. The plant was originally propagated via a leaf cutting, which in turn is where the offsets will develop once calloused. Plant: Dracaena parva x D. suffruticosa 'Fernwood' (originally Sansevieria)
Propagation
Via Seed, Division or Leaf Propagation. A word of advice is that if you take cuttings from variegated Sansevieria, the new growth will not have the variegated edges that many horticulturalists desire (i.e. yellow edges).
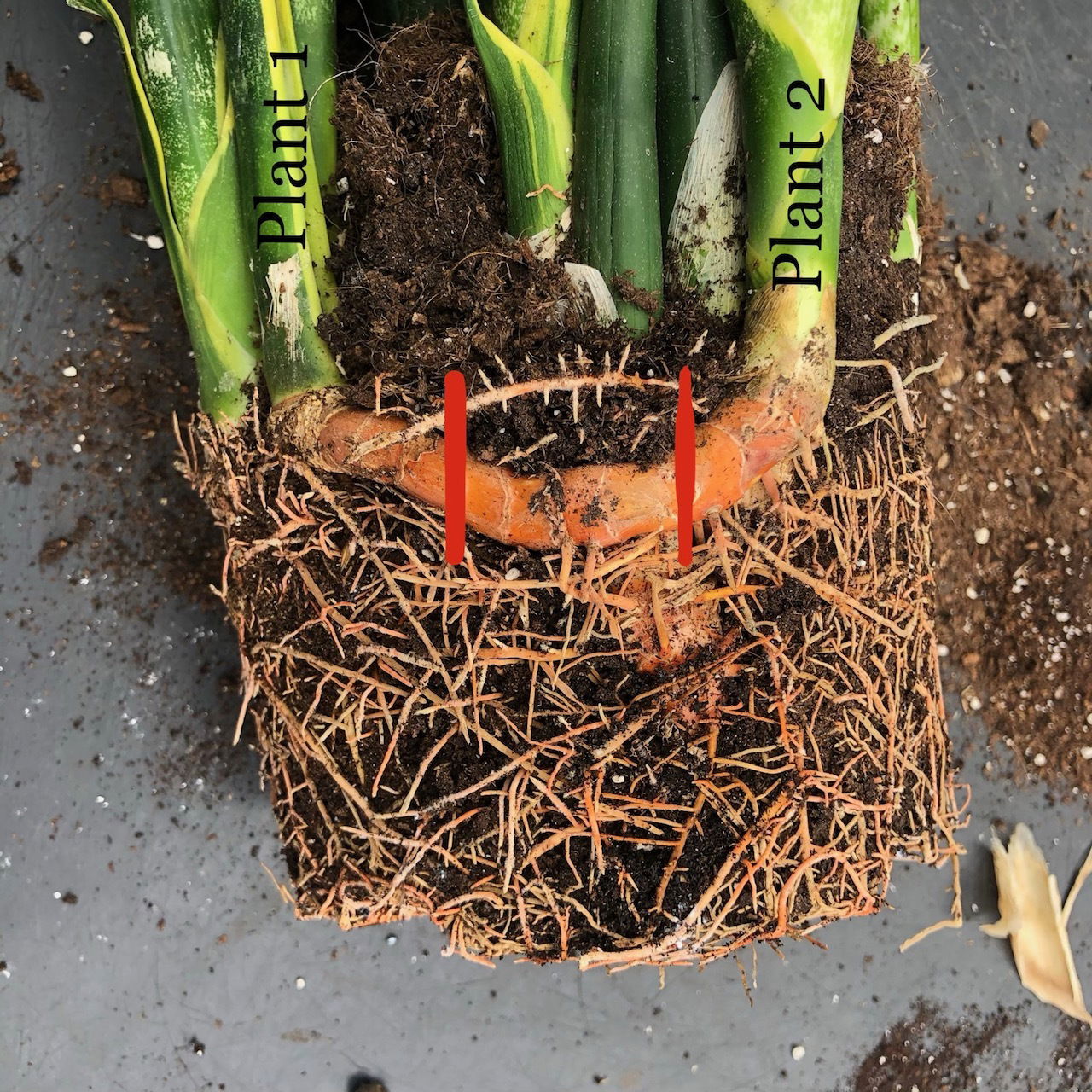 You can propagate this rhizome into two plants via the red lines. Be sure to use clean utensils and always water the plant 24hrs before propagation to avert 'Transplant Shock'. The middle section can be either discarded or be propagated by placing it an inch horizontally in soil.
You can propagate this rhizome into two plants via the red lines. Be sure to use clean utensils and always water the plant 24hrs before propagation to avert 'Transplant Shock'. The middle section can be either discarded or be propagated by placing it an inch horizontally in soil.
Rhizomatous Division (Easy) - For this method, it's best to divide in the spring or summer with the offshoots being at least half the mother plant's length of the blade. If you're unsure as to what they look like, have a look at the second image on this article. Take the plant out of its pot and place your hand in between the two growths; soil may have to be removed to get a better grip. While placing your fingers around to the nodal junction, gently push the offset downwards, supporting the mother plant. Once it snaps, cautiously separate the two roots systems, keeping great empathy in keeping the roots intact and damage-free. Place the new plantlet in a 'Cactus & Succulent' labelled soil and maintain the same care routines. If the offset doesn't have any roots, fear not - they'll soon develop if the compost is kept on the drier side of life. Never use a pot that is too big as a ratio of roots-soil that leans towards the latter will cause root rot and eventually plant death. For the first couple of months, allow all of the soil to dry out in between waters and provide a bright, indirect setting for best growth.
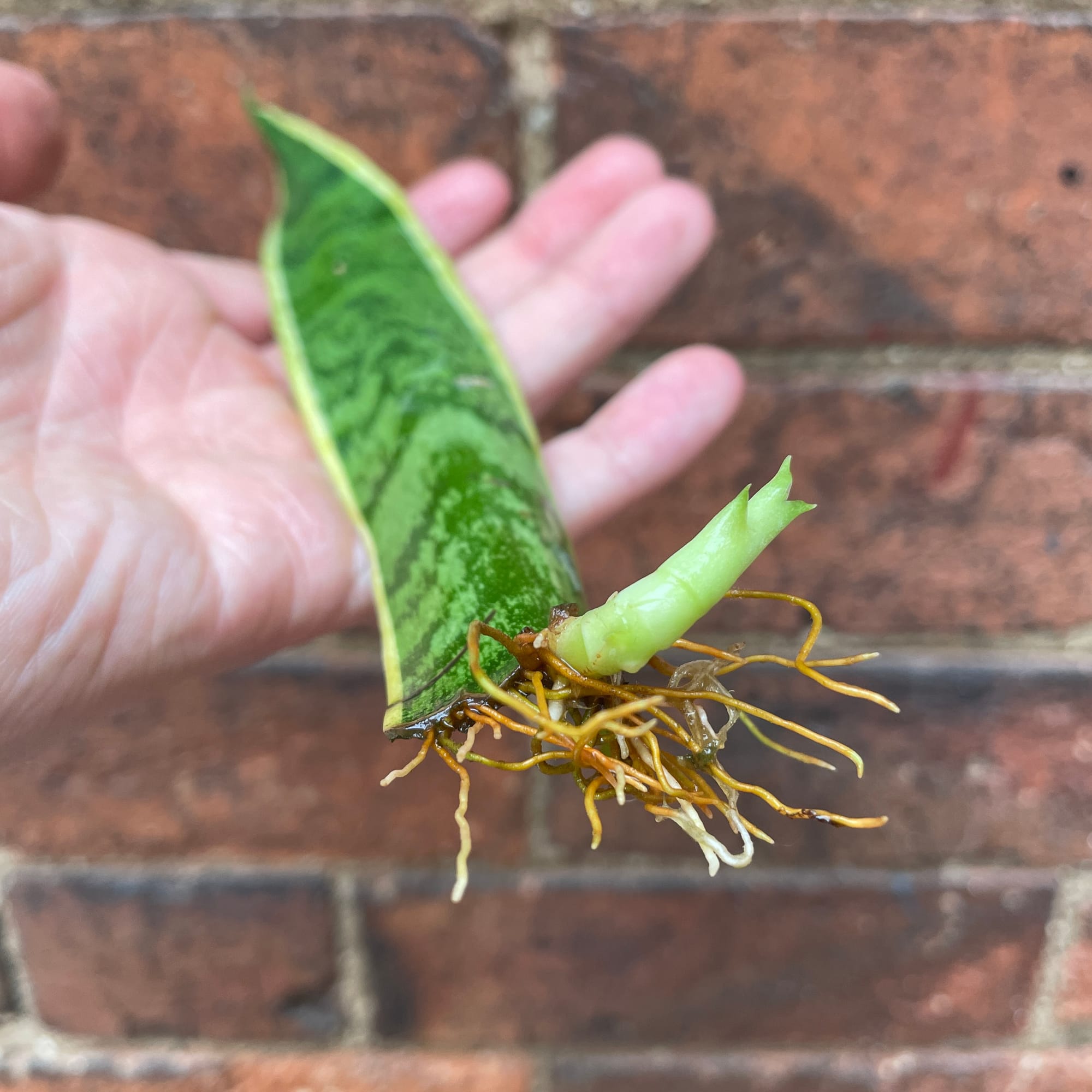 A perfect example of a water-grown Sansevieria leaf cutting that's ready to be potted up in soil. We recommend using a plastic pot (over a terracotta one) as the plants tend to grow better.
A perfect example of a water-grown Sansevieria leaf cutting that's ready to be potted up in soil. We recommend using a plastic pot (over a terracotta one) as the plants tend to grow better.
Leaf Cuttings (Easy) (Photo Above) - This propagation method is by far the most enjoyable, and the easiest way to duplicate the original plant. Leaves that are at least 15cm (6 inches) long and part of an established plant are most successful. To avoid making a mess of the serrations, use a sharp, clean knife and cut the leaf into three equal sections, all at least 5cm in length. Make sure you don't puncture the leaf by pressing down too hard with the knife - let the blade do the work. Once pruned, place the cuttings wound-down in lukewarm water (until 3cm of root growth and then into the soil) or immediately into a 'Cactus & Succulent' labelled potting mix, with a pot that has adequate drainage. Provide a bright, indirect setting with relatively moist soil, but be sure to allow the top half to dry out in between waters. You'll know if propagation has worked as the main body will stay green and firm, while unsuccessful specimens will turn yellow after a few days. New adventitious shoots will surface to the soil line after around eight weeks but may take longer if the conditions aren't optimal. After a month of the new leaves unfurling, transplant into a slightly bigger pot and treat it like a mature specimen with the care tips provided above.
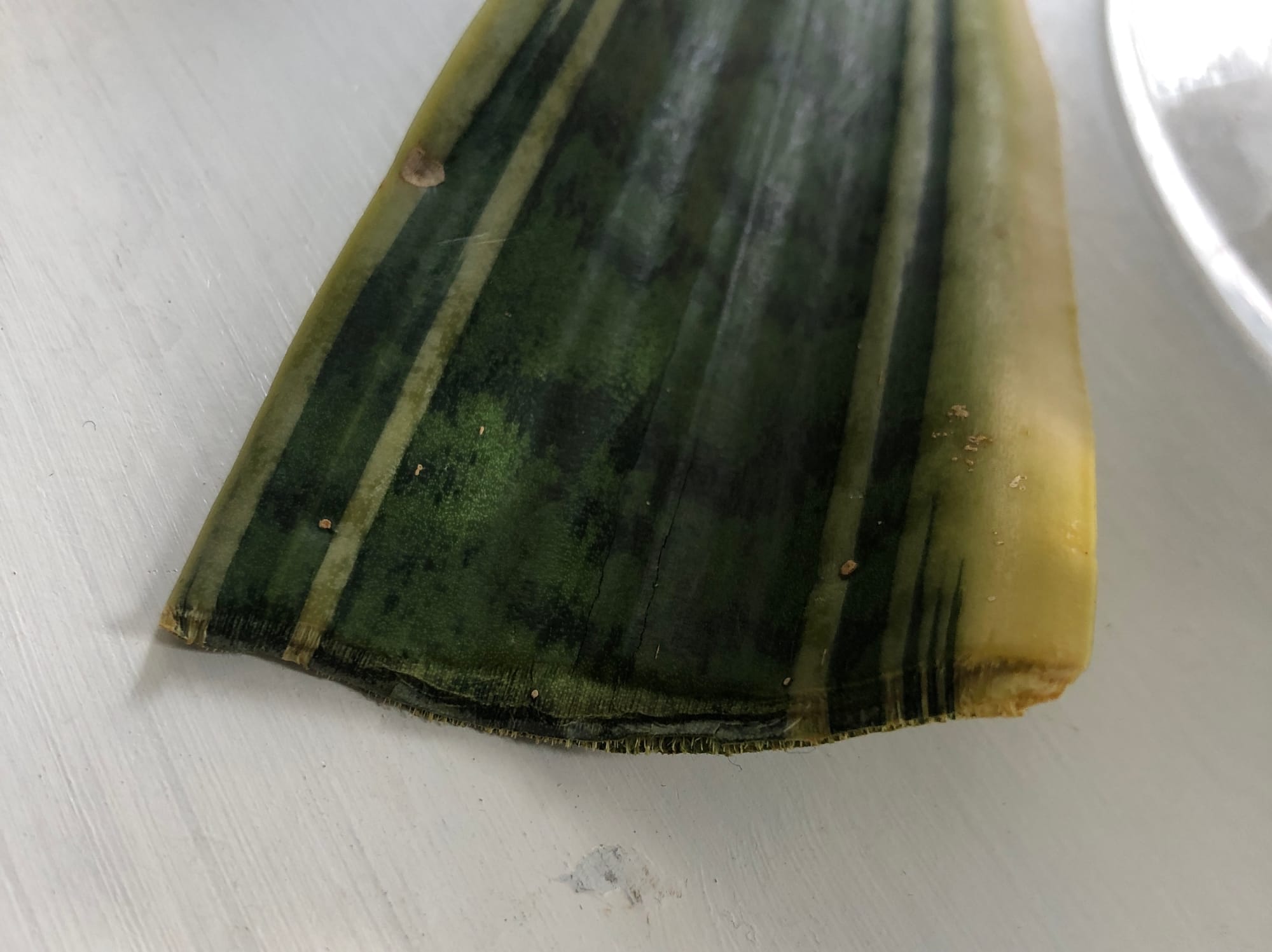 If you apply too much pressure with a knife whilst propagating the leaf, the wound will eventually close-up and it won't produce roots or a new stem of growth. We recommend applying as little pressure as possible when cutting, allowing the blade to do the work for us. If this has happened with your cutting, re-prune 3cm (1.5 inches) from the wound and try again!
If you apply too much pressure with a knife whilst propagating the leaf, the wound will eventually close-up and it won't produce roots or a new stem of growth. We recommend applying as little pressure as possible when cutting, allowing the blade to do the work for us. If this has happened with your cutting, re-prune 3cm (1.5 inches) from the wound and try again!
Flowers
A domestically grown Sansevieria might bloom within a few years of ownership if the soil is kept dry during the autumn and winter period. The sweetly-scented flowers are arranged in equal intervals along with the one-foot shaft that'll emerge from the plant's base. Each flower can last up to ten days, with the blooming process spread across several weeks. Pollinated flowers will produce bright orange berries that may be toxic to animals when eaten.
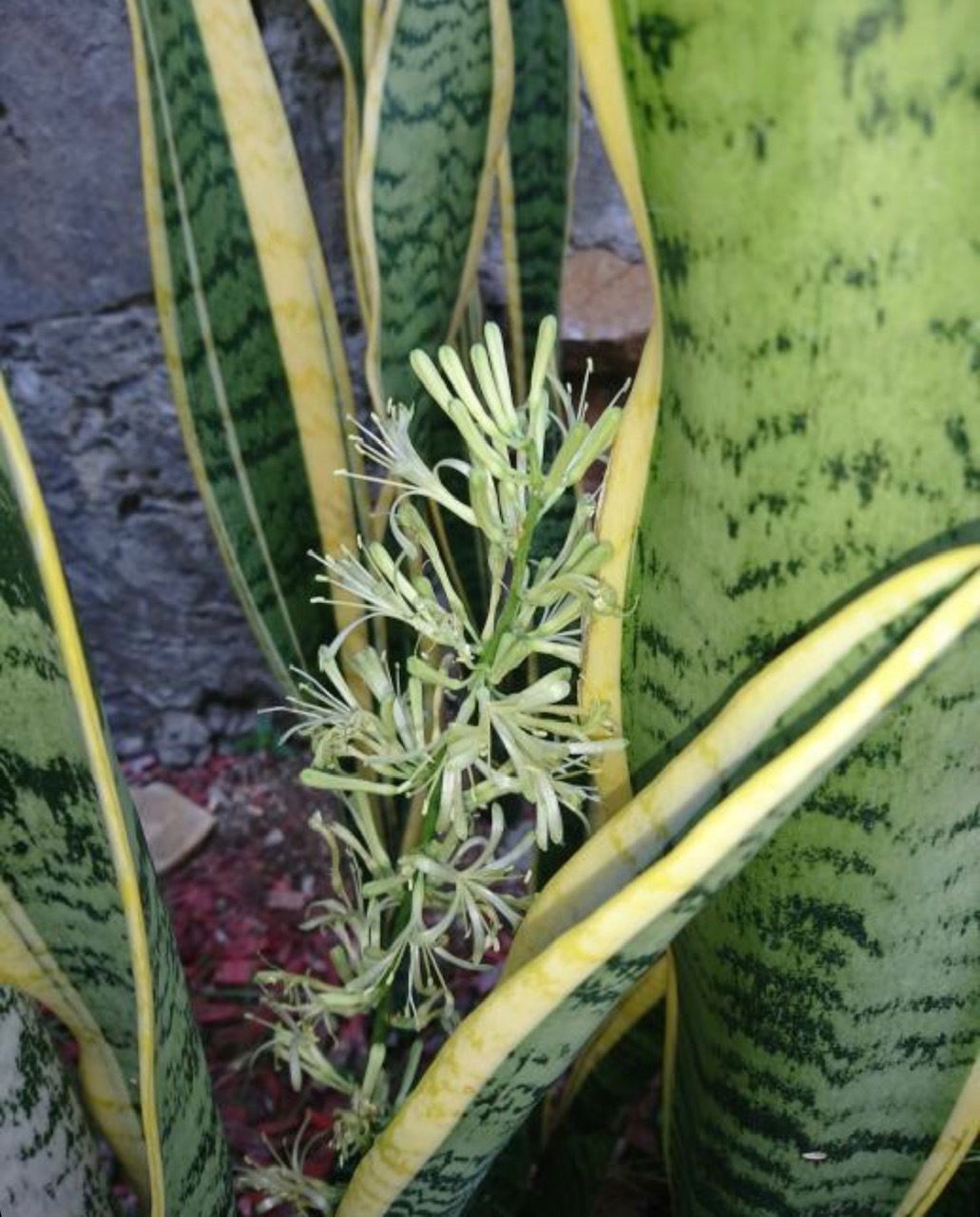 The inflorescence of a Sansevieria (Dracaena) trifasciata var. Laurentii
The inflorescence of a Sansevieria (Dracaena) trifasciata var. Laurentii
Repotting
Repot every three years in the spring, using a 'Cactus & Succulent' labelled potting mix and the next sized pot with adequate drainage. Sansevierias are a 'family plant' and therefore the mother plant can happily grow with its pups for many years, even if this means over-filling the pot. They prefer to be potbound as this will downplay the risk of over-watering (& root rot), so only repot if necessary or if you're interested in propagating the offsets to expand your spiky collection!
How to Repot
Hydrate the plant 24hrs before tinkering with the roots to prevent the risk of transplant shock. For those situated in a darker location, introduce extra amounts of perlite and grit into the lower portion of the pot to downplay over-watering risks. Click here for a detailed step-by-step guide on transplantation, or via this link to learn about repotting with root rot.
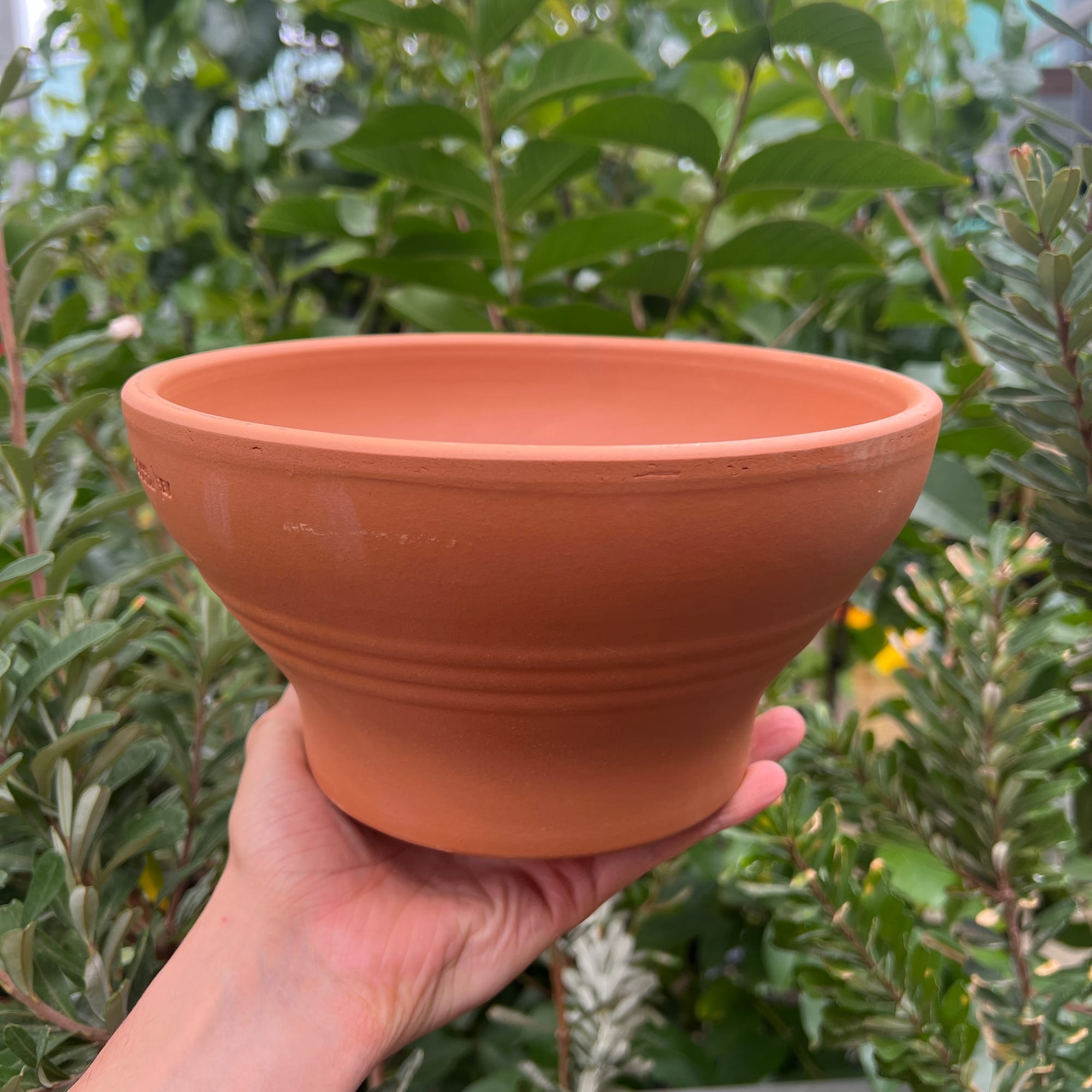 If you're interested in promoting more basal offsets (i.e. foliage), use a terracotta bulb bowl to complement the rhizomes' explorative horizontal nature - these can be purchased at most garden centres for low prices.
If you're interested in promoting more basal offsets (i.e. foliage), use a terracotta bulb bowl to complement the rhizomes' explorative horizontal nature - these can be purchased at most garden centres for low prices.
Pests & Diseases
Keep an eye out for mealybugs, spider mites, scale, thrips, whitefly & root mealybugs. Common diseases associated wth Sansevieria are root rot, red leaf-spot, botrytis & fusarium (pictured below) - click here to learn more about these issues.
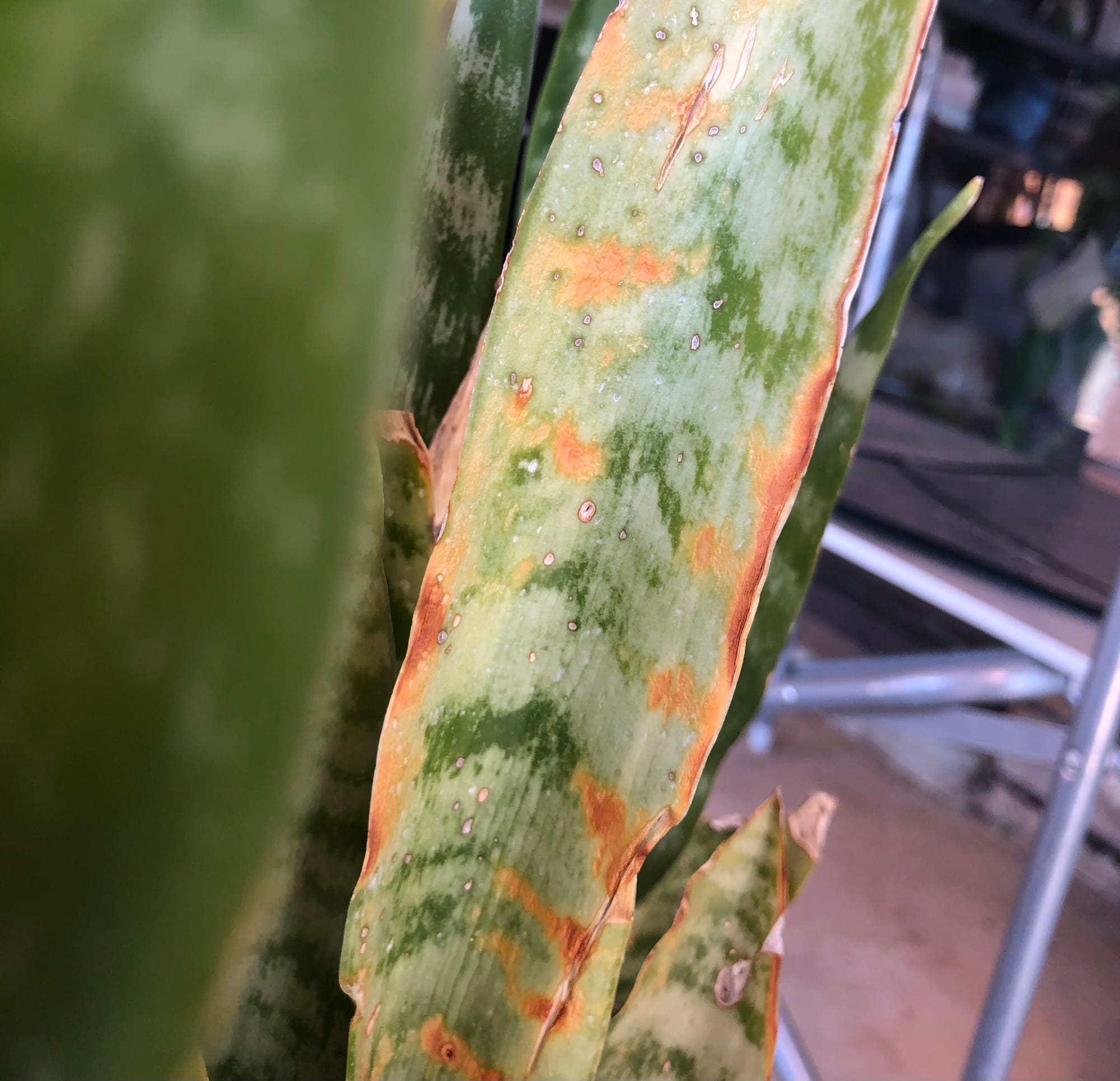 This may be a case of a disease called 'Fusarium'. We recommend removing the entire individual plant from the rest in your pot to avoid this spreading.
This may be a case of a disease called 'Fusarium'. We recommend removing the entire individual plant from the rest in your pot to avoid this spreading.
Toxicity
This plant is classified as poisonous due to high levels of saponins found in the leaves. If parts of the plants are eaten, vomiting, nausea and a loss of appetite could occur. Consumption of large quantities must be dealt with quickly; acquire medical assistance for further information.
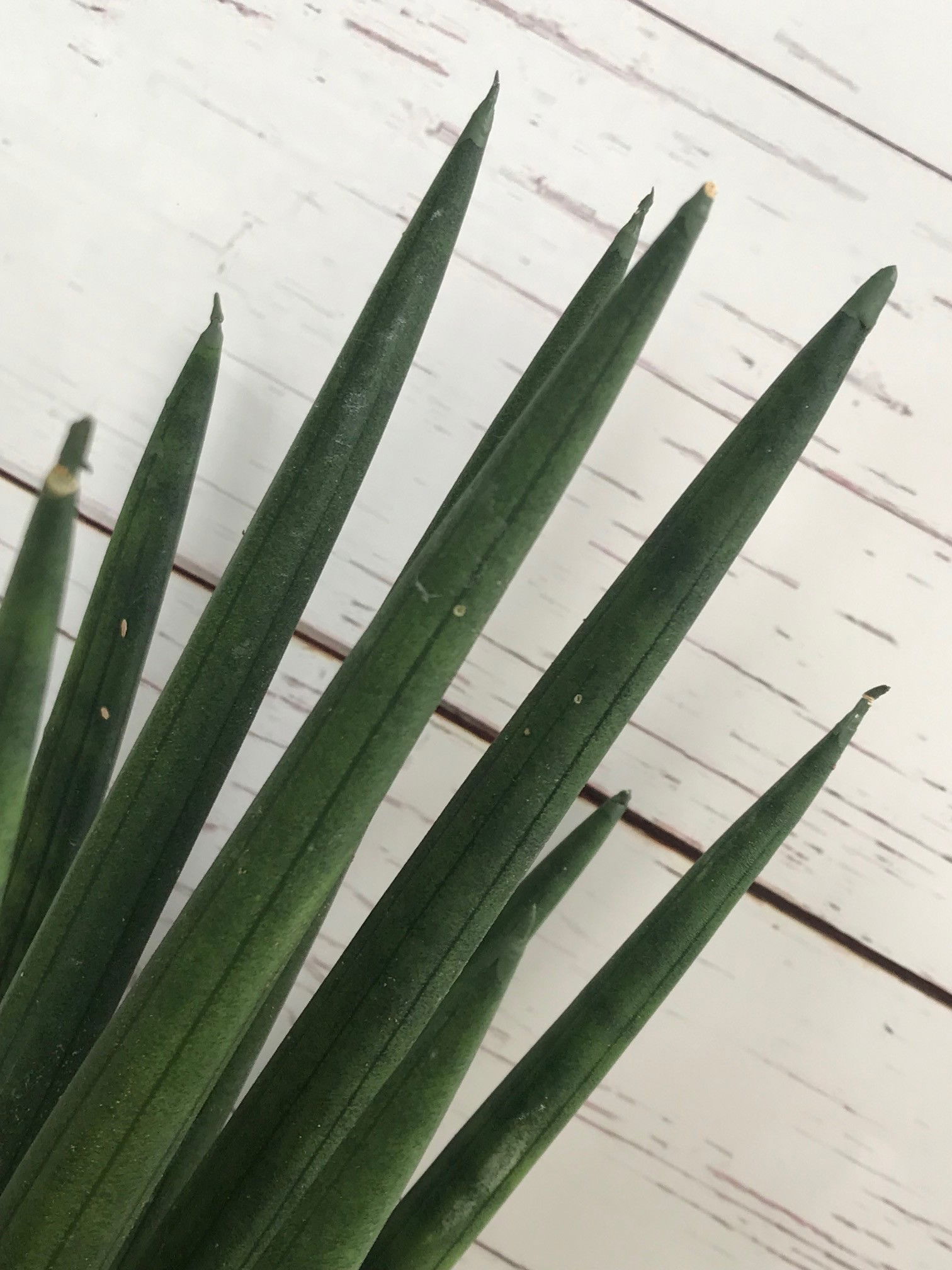 The Rocket Plant or African Spear Plant (Sansevieria cylindrica) is another fantastic species to grow as a houseplant. These can be grown in most rooms & locations in your home with no issues of environmental shock.
The Rocket Plant or African Spear Plant (Sansevieria cylindrica) is another fantastic species to grow as a houseplant. These can be grown in most rooms & locations in your home with no issues of environmental shock.
Retail Locations
Dobbies, IKEA, B&Q, Blue Diamond, British Garden Centres, Online Stores.

Book a 1-to-1 Call with THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™
If you need further advice with your houseplants, book an advice call with ukhouseplants' friendly and expert writer today! This can be done via a video or audio call on most apps, including Facebook, FaceTime & Skype. A ten-minute call costs £5.99 (US$7), or £15.99 for thirty minutes. You can ask multiple questions, including queries on plants, pests, terrariums, repotting advice and anything in between. Please consider supporting this service to keep ukhouseplants thriving!